Country Overview
Qatar has emerged as a key economic player in the Middle East. This sovereign state is bordered by the United Arab Emirates in the southeast and Saudi Arabia in the southwest. Qatar’s economy is traditionally dominated hydrocarbon but currently the country is attempting to reduce its reliance on oil and gas to become a knowledge-based economy while diversifying the opportunities further. Qatar ranks among the top countries globally in terms of GDP per capita, reflecting its economic strength and future prosperity.
To fuel and guide and expand this growth strategically and effectively, the country is currently pursuing its National Vision 2030. Under this vision, Qatar aims to evolve into a progressive society and growing country while ensuring a high quality of life for its citizens by 2030.
The vision is structured around four main pillars:
- Human Development
- Social Development
- Economic Development
- Environmental Development
With its strategic vision and the Government’s unwavering commitment to national development, the nation is creating exciting opportunities for investors as well as individuals.
Market Glimpse
Investors seeking growth potential and access to regional and global markets find Qatar an attractive destination. The country’s general budget of 2024 states that the non-oil revenues is estimation to reach QAR 43 billion in 2024, an increase of around 2.4% compared to 2023. On the other hand, the oil and gas revenues in 2024 are projected to be QAR 159 billion.
Qatar is actively promoting new economic sectors in the knowledge and digital economy. The Ministry of Communications and Information Technology (MCIT) is currently focusing on the e-commerce sector to drive the nation’s economic growth.
Qatar’s commitment to innovation and sustainable growth makes it an attractive destination for businesses seeking opportunities in the Middle East. According to Trading Economics, in the second quarter of 2024, the Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) has increased by 1598 QAR Million.
To attract more foreign investors and businesses, Qatar offers several incentives, such as:
- A legal environment based on English common law
- Transfers that can be made in any convertible currency
- Up to 100% foreign ownership
- Repatriation of profits
Along with all these advantages, businesses should be aware of certain challenges before setting up a new business:
| Potential Problems | Measures to Protect Business |
| Obtaining numerous permits from various authorities | Hire or consult local experts who will guide throughout. |
| Prevalence of scams | Confirm the reliability from official entities before proceeding. |
| Specific import restrictions | Consult with local customs authorities to navigate regulations. |
Transitioning from the wider economic context, we now turn our attention to the intricacies of payroll management, a critical component for any successful enterprise. This guide will explain the essential aspects of payroll, ensuring compliance and better operational efficiency
Payroll Compliance Essentials
Starting a business in Qatar involves several steps, Ministry of Commerce and Industry (MOCI) provides comprehensive information on the requirements and procedures for establishing different types of companies. After filling the relevant application form in MOCI website and submitting the required documents according to the chosen type of company.
Once the company is allowed to start its business operations, the employer needs to maintain compliance with the relevant laws to run the business smoothly.
The Ministry of Administrative Development, Labour and Social Affairs (MADLSA) is a government body responsible for overseeing policies related to Labor, employment and social development.
In this guide, the statutory details right from onboarding to offboarding of an employee will be discussed in depth. To start with, the links to relevant official sites are embedded below:
| Category | Regulation Number | Regulation Name |
| Social Security | Law No. (1) of 2022 | The Social Insurance Law |
|
Labour Law |
Law No. (14) of 2004 | The Labour Law |
| Law No. (17) of 2020 | Determination of the Minimum Wage for Workers and Domestic Workers | |
| Decision No. (25) of 2020 | Determining the Minimum Wage for Workers and Domestic Workers |
Onboarding Simplified
The onboarding process for employees in Qatar must follow the relevant labour laws and established standards to ensure compliance. Explore the essential best practices and legal requirements to ensure a compliant onboarding experience:
1. Employee Classification
| Types of Employees | Definition |
| Permanent employee | Employed under indefinite-term contracts |
| Temporary employee | Employed under fixed term contracts or for a specific project |
| Casual employee | Employed for a work which shall not take more than four weeks. |
| Trainee | Employed to learn the basics of a profession or a craft or to increase his knowledge or skills therein. |
Qatari workers shall have the priority in employment and non-Qataris may be employed when necessary.
As per Article 23, non-Qatari workers shall be employed only after the approval of the Department and after obtaining the work permits in the state in accordance with the rules and procedures prescribed by the Ministry.
Work permits shall be issued to non-Qataris upon the following conditions:
- There shall be no Qatari worker, qualified to perform the work for which a permit is required, registered with the Department registers.
- The worker shall have a residence permit.
- The worker shall be medically fit.
As per Article 25, the Minister may cancel the work permit granted to the non-Qatari worker in the following cases:
- If the employee fails to meet either of the conditions set out in Article 23.
- If the worker ceases from work for a period of more than three months for a direct personal reason and without a reasonable excuse.
- Work for an Employer rather than the Employer the work permit is issued for.
- Dismissal of the Worker as a disciplinary action
2. Employment Contract
Based on the employment type, there are 2 types of contracts:
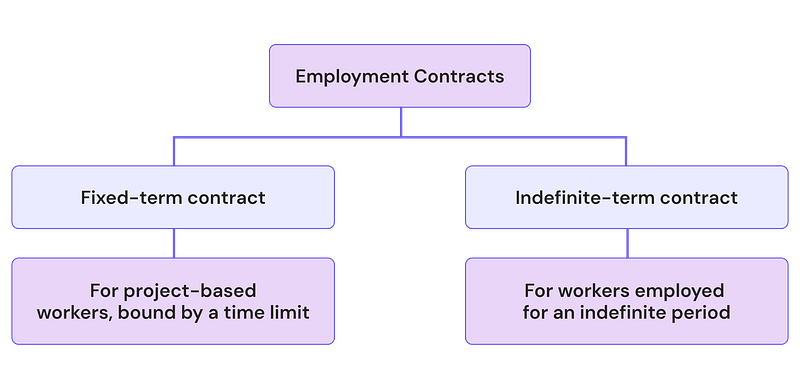
As per Article 38 of Labour law, the employment contract should be in writing mentioning all the legal information. The mandatory information include:
- Name of the employer & place of employment
- Name of employee, qualifications, address, nationality, place of residence & identity proof
- Contract type
- Date & place of signing the contract
- Job description
- Commencement date of the contract
- Duration in case of a fixed term contract
- Agreed Wages
- Payment method and date
Employment Contracts shall be in writing and ratified by the Department. It shall be made in three copies; each party shall receive a copy, and the third copy shall be deposited with the Department.
If it is a fixed-term contract, the duration of the employment contract shall not exceed five years, and such duration may be renewed to similar durations upon the agreement of the two parties.
3. Minimum Wages
- MADLSA regulates the minimum wage in Qatar. Law No. 17 of 2020deals with setting of minimum wage for workers and domestic workers.
- As per the Ministerial Decision No. 25 of 2020, the minimum wage which the worker or employee is entitled to is QAR 1,000 per month.
- If the employer does not provide adequate housing or food to the worker or employee, then minimum housing allowance is QAR 500 and minimum food allowance is QAD 300.
- The wage of a worker or employee shall not be less than the minimum wage provided and any agreement to the contrary shall be null and void.
- If the wage received by the worker or employee is not strongly determined, and the total of what they received per month is less than the minimum wage, the employer shall grant him an additional wage equal to the difference between what they received and the minimum wage.
4. Probation Period
- In Qatar, the probation periods may vary depending on the employment contract. However, the probation period should not exceed 6 months from the date of commencement of the work.
- The worker shall not be subjected to more than one probation period with the same employer. Either the employer or worker can terminate the employment contract during Probationary period.
- If either party terminates the contract without observing the notice periods stipulated in this Article, he shall pay the other party a compensation equal to the worker’s basic wage for the notice period or the remaining period thereof.
- In all cases, if the expatriate worker leaves the country without being bound by the provisions stipulated, they may not be granted a license to work for a period of one year from the date of departure
Workplace Protocols
Law No. (14) of 2004 (“Labour Law”) stipulates all the statutory regulations regarding employees to ensure they are treated fairly and protected from being exploit.
1. Working Hours
Article 73 of the Labour Law stipulates the standard working hours in Qatar:
| Maximum Working Hours |
| 8 hours/day |
| 48 hours/week |
Note: The working hours may vary sector wise.
During the month of Ramadan, the working hours reduces to:
| Maximum Working Hours |
| 6 hours/day |
| 36 hours/week |
2. Breaks
The working hours shall include an interval or more for prayer, rest and eating, and it shall not be less than one hour and not more than three hours.
As per Article 97, the lactating worker shall be entitled to one hour break for a period of year starting after the expiration of the maternity leave.
3. Rest Day
Employers are obliged to provide a weekly rest day for not less than 24 consecutive hours. Friday is the regular weekly rest day for all employees except shift workers.
4. Overtime
If the employees working hours exceed the above-mentioned standard hours, then they are entitled to overtime pay.
The total actual working hours per day shall not exceed ten hours, unless the work is necessary to prevent a gross loss or dangerous accident or to repair or mitigate the effects resulting from such loss or accident.
The employees must receive the normal hourly wage with an additional pay of 25% of the hourly wage.
If an employees work on the weekly rest day, they are entitled to their basic daily wage with an additional pay of 50% of the wage.
| Overtime Wages | |
| Normal working days | Basic wage + 25% of basic wage |
| Weekends or rest days | Basic wage + 50% of basic wage |
5. Night Work Pay
The Employer shall also pay the employees working between 9 p.m. and 3 a.m., an amount of basic wage plus a payment not less than 50% thereof, except workers working on shift schedules.
6. Leaves Entitlement
As per Article 78 of Labour Law the employees are entitled to get paid religious and public holidays listed below:
| Public Holidays | Date | Number of Days |
| Eid Al-Adha | The dates for this holiday are subject to variation each year | 3 days |
| Eid Al-Fitr | The dates for this holiday are subject to variation each year | 3 days |
| Independence Day | December 18 | 1 day |
- Apart from above, Employer shall provide 3 working days as per their convenience.
- Furthermore, the employees of Qatar are entitled to several other paid statutory leaves as provided below:
| Leave Type | Maximum Entitlement |
| Annual leave* (Article 79) | 3 weeks if Service period is less than 5 years
4 weeks if service period is 5 years or more |
| Sick leave** (Article 82) | 6 weeks |
| Hajj leave (Article 83) | Maximum 2 weeks to Muslim workers, usually unpaid |
| Maternity leave (Article 96) | 50 days*** |
* An employee shall be entitled to leave for fractions of the year in proportion to the period spent in service (Pro-rata). Public holidays that fall within annual leave period are not counted as part of annual leave.
** Sick leaves are granted only after completing 3 months. The employee shall be paid full wage if the sick leave does not exceed two weeks. If the sick leave extends thereafter, half of the wage is paid to the employer for another 4 weeks. Any extension after this is unpaid.
*** The period following the delivery shall not be less than 35 days. If the remaining period of the leave after delivery is less than 30 days, the female employee may be granted a complementary leave from her annual leave, otherwise, the complementary period will be unpaid.
Holiday Pay
If work conditions require employees to work on any of the public holidays, the employer is obliged to provide compensation. This can be in form of a day off for each holiday worked or payment for that day at the regular wage rate, plus an additional increase of at least 50% of the basic wage for that day.
7. Event-based Compensation
As per article 108 of Labour Law ,if the employee dies while working or because of the work, or he sustains a work injury, the employer or the acting person shall immediately report the incident to the police and the Department.
The report shall include the name, age, profession, address and nationality of the worker, and a brief description of the incident, the circumstances thereof, and the procedures taken for the rescue and treatment thereof.
| Compensation for Injury | Compensation for Death |
| An amount equivalent of full wage throughout the period of illness or for 6 months and half wage for another 6 months if the treatment period exceeds. | Compensation will be calculated based on provisions of Islamic laws. |
| Medical rehabilitation costs | Any other financial entitlements at the option of an employer |
The right of an employee to claim compensation for the incapacitation or death shall lapse after one year from the date of the final medical report containing the occurrence of the incapacitation resulting from the injury or the confirmation of the occurrence of the incapacitation because of any of the occupational diseases listed in the schedule No. (1) of labour law or from the date of the death of an employee.
8. Other Benefits
Although there are no other statutory benefits available, the employees may receive one-time or additional payment benefits, subject to their employment contract, such as:
- Bonuses
- Commissions and other supplemental wages
- Health Insurance
Salary Essentials
In Qatar, wages must be paid within 7 days from due date through Wage Protection System (WPS) as per Decision of the Minister of Labour and Social Affairs No. (4) of 2015. As per Article 66 of Labour Law, all the wages and other amounts of the worker shall be paid in the currency of Qatar. The Employer shall transfer the wage to the employee’s account in any financial Institution in the State.
1. Salary Components
Various salary components are commonly included as part of an employee’s gross salary, the table below provides an overview of the various salary components that constitute the salary structure in Qatar payroll:
| Salary Component | Definition |
| Basic wage | The average of what is paid to the worker for the work he performs during a particular period, or on the basis of piecework or production, and it includes the annual bonus only. |
| Allowances | It is a regular additional payment given to employees alongside the basic wage. For instance:
|
| Others | The non-fixed portion of the salary, for instance:
|
| Social Security Contribution |
|
| End-of-Service Benefits | Gratuity to be calculated upon termination of an employee. |
2. Payslip Components
In Qatar, there are no legal stipulations regarding the format, these payslips typically include the following components:
- Basic salary
- Allowances
- Deductions
- Net salary
- Leave encashments
- Loans or advances
- End-of-service benefits
Decoding Deductions
1. Withholding Taxes
Qatar does not have any income tax to be paid by employees. Therefore, the employers are not required to deduct any withholding tax.
2. Social Security
All Qatari citizen employees generally make contributions to Qatar’s social insurance system. All the covered employees must also be over the age of 18 with work contracts lasting at least one year.
Employees must contribute a portion of the basic salary, social allowances, housing allowances (subject to QAR 6,000) or any other similar allowances (‘Salary’) to General Retirement and Social Insurance Authority (GRSIA) monthly.
The following are the contribution rates as per Law No. (1) of 2022:
| Contribution Schemes | Employee Contribution | Employer Contribution | Maximum Salary Capping (in QAR) |
| Monthly Contribution | 7% | 14% | 100,000 |
This contribution should be deducted and remitted by the employer to GRSIA.
Insurance Protection Extension System
Qatari employees working in GCC countries subject to the protection extension system. The contribution is calculated on Salary.
Employers in Qatar are required, for each of their employees working in Qatar whose home country is another GCC country, to deduct any applicable contributions from the employee’s wages and make any applicable employer provided contributions based on requirements of the pension or retirement insurance program of the employee’s home country.
Contribution rates vary for nationals of each GCC country working in Qatar. The Insurance Protection Extension System specifies the condition for monthly contribution for Bahraini nationals, Omani nationals, Kuwaiti nationals, Saudi nationals and Emirati nationals. The extension system also sets out the condition for GCC nationals working in Government Sector. The employer must remit those contributions to a bank account designated by the applicable social insurance agency of the employee’s home country.
Reporting
| Reporting | Due Date |
| Registering with GRSIA | Within 14 days after starting of business |
| Payment of contribution | Payments are due on the 5th day of the month following the month for which they are due. |
| Submission of wages and contributions | In January of each year, employers must submit data on employee wages and contributions. |
Non-compliance
Penalties are assessed on late and incomplete filings and payments:
| Type of Non-compliance | Implications |
| Late payment | Penalty of 2% of the outstanding contribution rate for each month until the payment is complete. |
| Failure in registering any employee | Penalty of 10% of the total value of the contribution payable |
| Discrepancies in calculation | Penalty of 10% of the total value of the contribution payable |
3. Minimum Take Home Pay
- As per Article 60 of Labour Law, the total amount deducted from worker’s Basic pay in addition to bonuses, allowances and compensation paid (Wage) for disciplinary penalties and other reasons shall not exceed the Wage for five days per month.
- Any part of the Wage to which the worker is entitled shall not be attached or withheld, unless in the execution of a judicial ruling. In case of judicial ruling, alimony debt shall have priority over all other debts, and the total of the attached amounts must not exceed 35% of Wage of the indebted worker.
- The employer shall not charge any interest on loans provided to the worker and shall not deduct more than 10% from the worker’s Wage as repayment for such loans.
- As per Article 71, if an employee causes any loss, damage or destruction to machinery, equipment or products of the establishment, due to their fault, shall be obliged to compensate the employer for the damage provided that the obligation of the worker for the compensation shall be preceded by an investigation.
- The employer may deduct the compensation amount from the worker’s wage, provided it does not exceed seven days Wage in a month.
The total deductions of a worker should not exceed 50% of the Wage. Any excess deduction needs to carry over to the following month or months.
Seamless Offboarding
Being mindful of the offboarding process is equally important. Offboarding must maintain compliance with the nation’s Labour Law to avoid any serious consequences.
If the Employment contract is terminated for any reason, the employer shall pay the Basic pay in addition to bonuses, allowances and compensation paid (Wage) and other amounts to which the employee is entitled before the end of the day following the day on which the contract is terminated, unless the employee leaves the work without giving the notice.
In this case, the Employer shall pay the Wage of the employee and all other amounts to which they are entitled within a period not exceeding seven days from the date of leaving the work.
The Employer shall upon the expiration of the contract:
- Give the Worker upon his request, without any charges, a service certificate indicating the date of commencement, and the termination date of his employment, the type of Work he was performing and the amount of Wage he was receiving.
- Hand over to the Worker what he deposited therewith of certificates, documents and others
End of Service Gratuity (EOSG)
As per article 54 of Labour Law, EOSG will be calculated based on below formula irrespective of the reason of separation:
- Minimum of three weeks of employee’s last basic salary for each year of service. For partial years beyond the first, gratuity is prorated based on the months worked.
- EOSG is not calculated if an employee’s service period is less than 1 year.
- In the event of any outstanding amounts from an employee, employers may deduct it from the EOSG.
- An employee’s service is considered continuous if they are rehired within two months of termination and are terminated from an organization for reasons other than those which leads to immediate dismissal by an employer.
1. Retirement
As per Article 24 of social insurance law, an employee gets retired upon reaching the age of 60 years. If the contract is terminated without observing these periods, the one who terminates the contract shall pay to the other party a compensation equal to the worker’s basic wage for the notice period or the remaining period of it.
Upon retirement, the employee is entitled to receive the following benefits:
- Full pay for the notice period
- Compensation for any unused holiday entitlement
- Repatriation expenses if the employee is leaving the Qatar unless he has already joined the service of another employer.
- End of Service Gratuity (EOSG)
The employer maintaining a retirement system or any similar system which secures for an employee a greater benefit than the end of service gratuity to which the worker is entitled shall not be obligated to pay the end of service gratuity in addition to the benefit he offers under the system referred to.
If the net benefit accruing to the employee is less than the end of service gratuity, the employer must pay to the employee the end of service gratuity and must return any amount whereby the employee might have contributed to the system referred to, and the employee may choose between the end of service gratuity and any pension he is entitled to under such system.
2. Resignation
Employees can resign from their positions, provided they adhere to the notice period. In Qatar, the length of service determines the length of notice periods.
Follow the below given table for details:
| Length of Service | Duration of Notice Period |
| 1 to 5 years | 1 month |
| More than 5 years | 2 months |
The worker may terminate the employment contract during the probationary period, provided the following is observed:
- If the worker wishes to work for another employer by informing at least one month before the date of terminating the contract.
- If the worker wishes to terminate the contract and leave the country, he must notify the employer in writing of his desire to do so in accordance with the agreed upon notice period, provided it does not exceed two months.
The worker may, as per Article 51 of Labour Law, terminate the Employment Contract before the expiration of its duration if it is a fixed-term contract, and without notifying the employer if it is an open-ended contract, along with reserving his full right to the end of service gratuity.
Upon resignation, the employee is entitled to receive the following benefits:
- Full pay for the notice period
- Compensation for any unused holiday entitlement
- End of Service Gratuity
3. Dismissal
Notification to MADLSA
The employer shall, before terminating the employment contract for reasons of an economic or structural nature or other reasons not related to the employment contract, notify the MADLSA before at least fifteen days from the date of termination, and shall submit a written statement of the reasons for termination, the number of workers likely to be affected by the termination, their categories, the period during which the termination is intended to be implemented, and other relevant information requested by the MADLSA.
As per Article 61 of Labour Law, the employer may dismiss the employee without notice if the employee has represented false documents or contravenes the rules of the organisation or the employee is convicted by a final judgement where employee shall be entitled to receive the below:
- Compensation due.
- Employer shall reserve the right to either pay the EOSG or may deny the same, in specific cases.
Upon dismissal for reasons other than as per Article 61, the employee will be entitled to receive the following benefits:
- Full pay for the notice period
- Compensation for any unused holiday entitlement
- Repatriation expenses if the employee is leaving the Qatar unless he has already joined the service of another employer.
- End of Service Gratuity (EOSG)
Before appealing the sanction imposed on them, employees should raise their grievance to the employer before the competent court within 7 days from the date of being informed thereof.
If the dismissal is unfair, the committee shall either cancel the dismissal and reinstate the work of an employee and pay wages during the period of dismissal or to compensate an employee by a reasonable compensation.
Conclusion
Qatar stands as a beacon of economic growth and opportunity in the Middle East, supported by the effective government policies. The country’s commitment to continuous progress leading the nation to rise as an attractive hub for international enterprises. However, managing payroll in Qatar comes with its own unique challenges. Navigating the intricacies of local labour laws, social security contributions, and statutory reporting demands a comprehensive and efficient payroll system. Investing in advanced payroll solutions and being aware of regulatory updates are crucial for ensuring compliance and effective payroll management in Qatar.



