Table of Contents
India has a network of laws and statutes that every organisation must comply with. Statutory Compliance means that all actions that an organisation takes must adhere to the provisions set by the law. Therefore, processing employees’ payroll and social security benefits must also comply with the relevant laws. The employer’s treatment of the organisation’s employees should also obey the relevant state and central labour laws. Non-compliance would invite penalties, fines, and legal action against the organisation. Following the tenets of the labour laws is beneficial to the employer, employee, and the organisation.
Statutory compliance is important from both the employer’s and the employee’s perspectives. Many labour are laws created for the employee’s benefit, such as the Industrial Relations Act, Women and Child Safety, social security, minimum benefits, Health and Occupational Safety, etc. Non-compliance with any of the above-mentioned laws means that the Government of India will take action that may threaten the company’s legal existence.
The HR departments and employers have the legal responsibility to ensure legal compliance with these laws. The Government of India conducts statutory audits periodically to ensure and verify such compliance. To maintain their corporate existence and avoid all legal hassles, companies should, as a matter of course, ensure complete compliance.
For the employee
For the employer
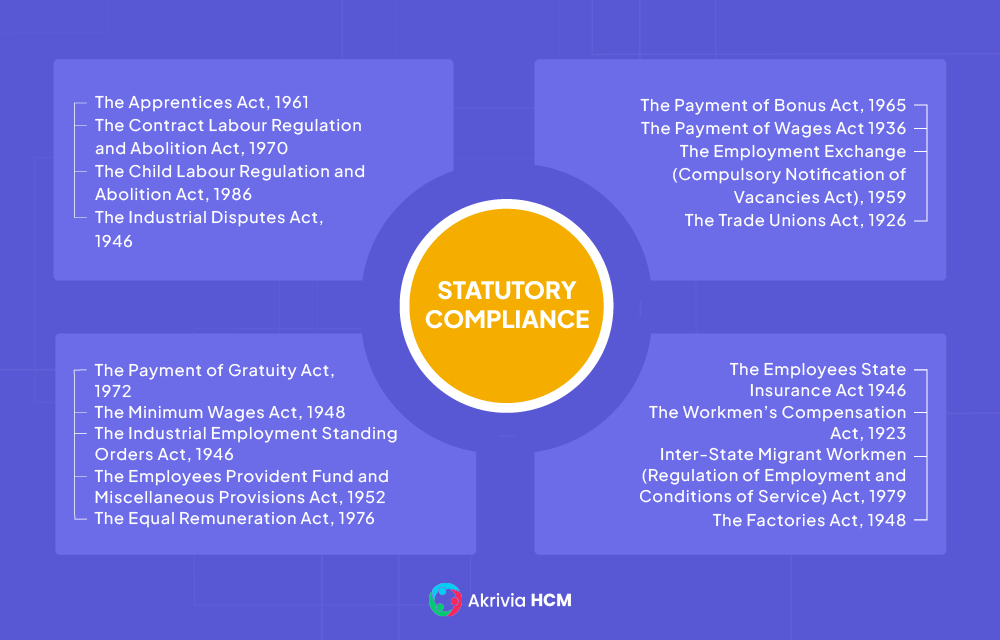
The list of important Acts which affect an organization and its HR function is enclosed below:
Key Provisions of Statutory Compliance in India:
| Income Tax Slabs | Old Tax Regime | New Regime | ||
| Citizens below 60 years | Senior citizens above 60 years | Super senior citizens above 80 years | All categories | |
| Rs 0–2.5 lakhs | No Tax | No Tax | No Tax | No Tax |
| Rs 2.5–3 lakhs | 5% rebate under Section 87 a | No Tax | No Tax | 5% rebate under Section 87 a |
| Rs 3–5 lakhs | 5% rebate under Section 87 a | No Tax | ||
| Rs 5–7.5 lakhs | 20% | 20% | 20% | 10% |
| Rs 7.5–10 lakhs | 20% | 20% | 20% | 15% |
| Rs 10–12.5 lakhs | 30% | 30% | 30% | 20% |
| Rs 12.5–15 lakhs | 30% | 30% | 30% | 25% |
| Rs 15 lakhs and above | 30% | 30% | 30% | 30% |
It is the responsibility of HR departments in organizations to make the deductions and make payments to the Income Tax department.
The formula of gratuity for 2 conditions are:
1. Companies covered under the Act
Gratuity amount= (15 x last drawn salary x tenure of working)/26
2. Companies not covered under the Act.
Gratuity amount= (15 x last drawn salary x tenure of working)/30
Akrivia HCM provides the best digital HR solutions to enterprises, with one of Top Payroll Software in India to help you transition smoothly from paper- and file-based working to a digital, mobile solution. Akrivia HCM’s solution provides a smooth, seamless changeover to an AI-based HR management system that encapsulates all personnel management functions under one roof.
Let’s Recruit, Reward, and Retain
Your Workforce Together!
