Table of Contents
Grievance occurs when employees’ discontentment rises at the workplace. There may be several factors that affect the employees and trigger it. Human resource managers need to properly deal with it as early as possible to avoid adverse impacts on employee performance and minimize the turnover rate. Familiarity with it and its types empower HR managers to develop procedures of grievance redressal to improve employee morale.
Let’s read about grievances, types, causes, and ways to deal with them.
It is a problem and concern raised by an employee to an employer. The employee raises it due to dissatisfaction with the employer’s policies, poor working conditions, and legal issues.
An employee’s grievances may or may not be valid. However, its presence signifies the remarkable gap between the employee’s expectations from the organization and the actual working conditions provided to that employee.
The causes of grievances are listed below:
Genuine grievances are also known as factual grievances. When the reason for raising it is accurate and raised on valid employment reasons, they are known as fact-based grievances. In this, the employers are liable to make significant changes or the required improvements to provide redressal.
The fictitious grievances do not arise on valid grounds. Due to the lack of factual evidence backing, the employer cannot be held responsible for it because these are primarily imaginary only with no impact on employee morale.
Interpersonal issues, discontent, and disagreement trigger most workplace grievances. As organizations work with a diverse workforce with different views and approaches to problems, there is always room for interpersonal grievances unless they are proactively handled and resolved by the employer.
These issues form from interpersonal relationships and dynamics at the workplace. Most interpersonal issues that lead to grievances are discrimination, bullying, and harassment. Diversity inclusion leads different people to work in a commonplace and causes dissatisfaction.
When an employee feels dissatisfied with any work-related issues and reports them to the supervisors or the top management, it comes under an expressed grievance. These grievances are known to people managers.
The implied grievances are not reported but noticed by the employer from employees’ responses and working situations. These are hidden grievances that need proactive focus before such grievances can turn into detrimental factors impacting the performances of parties involved in the workplace.
When an employee feels dissatisfied with the policies and working regulations of the employer, these come under policy-based grievances. Either existing or newly-introduced policies cause these grievances.
There can be several reasons for policy-based grievances, like work timings, working hours, pay and overtime pay structures, compensation and incentive scheme leave policies, dress code, unequal workload, etc.
Individual grievances occur when an employee is discontented with the business environment issues and reports them to the management. The individual-level grievances exist due to interpersonal problems, unsatisfactory policies, and wrong individual perceptions towards the employer.
The collective grievances occur when any particular department, team, or employee group is not pleased and express the same to the respective authorized personnel. The group grievances arise due to improper integration between departments, unfair treatment, or other issues affecting a group of employees collectively.
Whistleblowing grievances are also referred to as “good to know” grievances. In this type of grievance, an individual faces a dilemma between personal ethics and employer policy, thus becoming discontented.
The employer should not avoid considering whistleblowing grievances as it provides an opportunity to improve transparency at the workplace and motivate the employees to take up leadership in crucial issues.
Grievances should be dealt with proactively, rather than waiting for them to be brought to management’s attention. A proactive approach to grievance redressal helps the company modify those factors that are responsible for grievance.
Management can identify grievances in four ways: conducting exit interviews, soliciting comments through a gripe box system, conducting opinion surveys, and maintaining an open-door policy. Let us examine the information generated through these methods.
There are a lot of reasons for writing a grievance letter. Employees write it for the bad behavior of their colleagues, dissatisfaction within the organization, and many more. Since it is a written document, there are many things that can concern and raise questions against you. It’s better to be concise and formal. Below mentioned points should be included in your grievance letter:
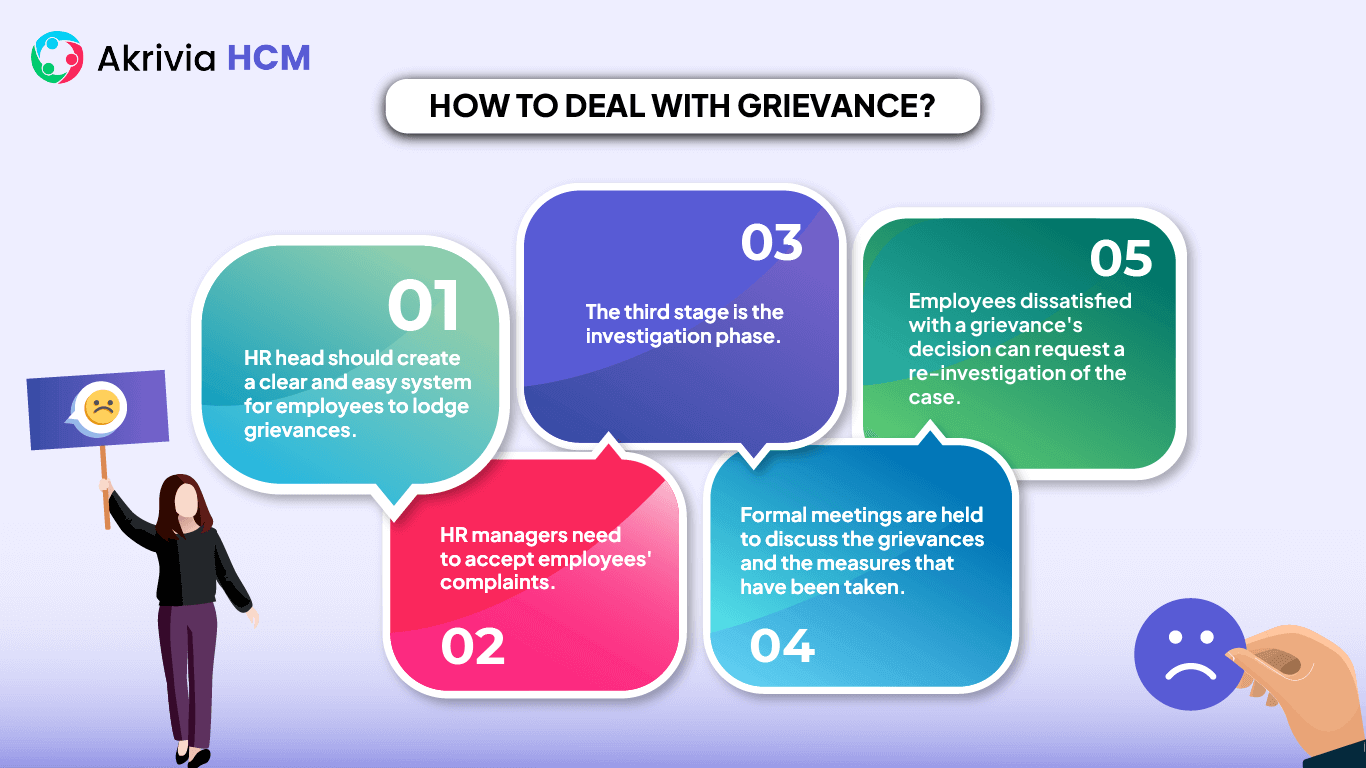
Dealing with grievances requires several steps to be followed sequentially:
There are many differences between a complaint and a grievance. The primary one is that the complaints involve small-scale issues, mostly related to any deviation, while grievances involve large-scale problems in the workplace. These can be over policies and functioning of the organization as well.
The employer does not need to provide written responses to the complaint. The complaints get documented for administrative purposes and investigations into the root cause. Resolving complaints improves the day-to-day functioning of an individual or an organization.
An organization’s HR managers need to provide a written response to the grievances covering time frames, transform policies, and eliminate the grievance issues. Resolving it helps address issues that are likely to impact the long-term performance of the employer.
Grievance management contributes to elevating satisfaction and raising morale among employees. The HR managers strive for a robust platform that helps manage an organizational workforce.
Akrivia automation’s employee management system helps to develop a transparent payroll system and conducts surveys to develop transparency to avoid major causes of grievances.
It provides you with new-age technology and the latest HR suite to improve quality and standards in managing human resources effectively and efficiently and eliminate a higher turnover rate.
Let’s Recruit, Reward, and Retain
Your Workforce Together!
