Table of Contents
Employees are still confused about CTC and gross salaries. Understanding the difference between CTC, basic pay, net income, and gross salary is important. Some working professionals understand the difference between these two terms, but most people have many questions about them. Here is an explanation of the meaning of Cost to Company and how it is different from other salary types.
CTC is the amount spent by the company on hiring an employee.
It is the sum of salary and additional benefits that an employee gets while working within a company. It is the complete package and annualized salary of an employee offered by the employer.
To understand it thoroughly, employee costs to the company are the total sum that the employer spends on him. It is the amount bears by the company to sustain and hire an employee.
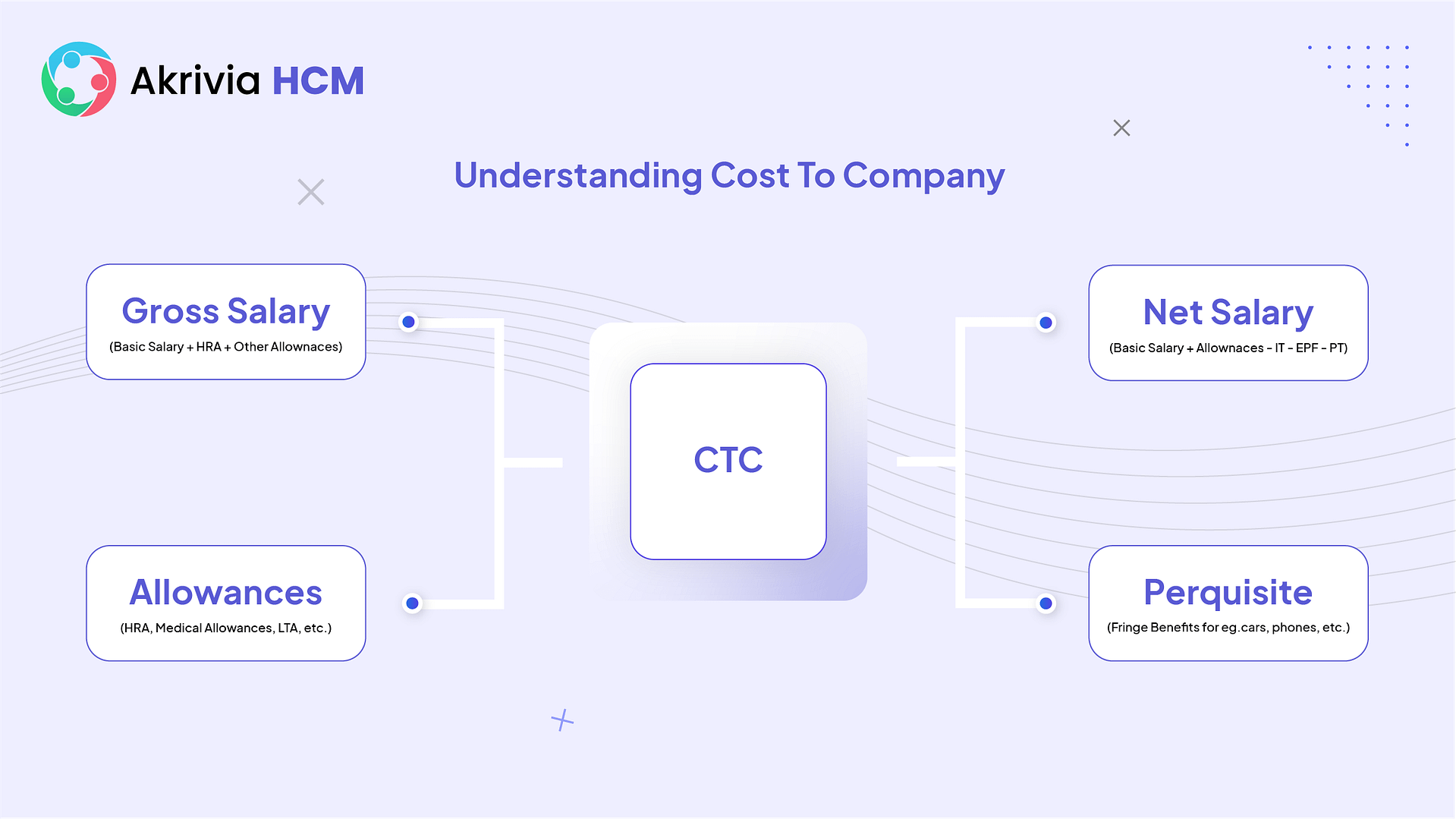
CTC is the wholesome benefit that employees withdraw from the company in tangible and intangible forms.
CTC is not a fixed pay. It is the variable pay as the indirect and direct expenses of the company on its employees may change yearly.
An employee doesn’t necessarily receive the CTC in cash as additional benefits are received in an intangible form.
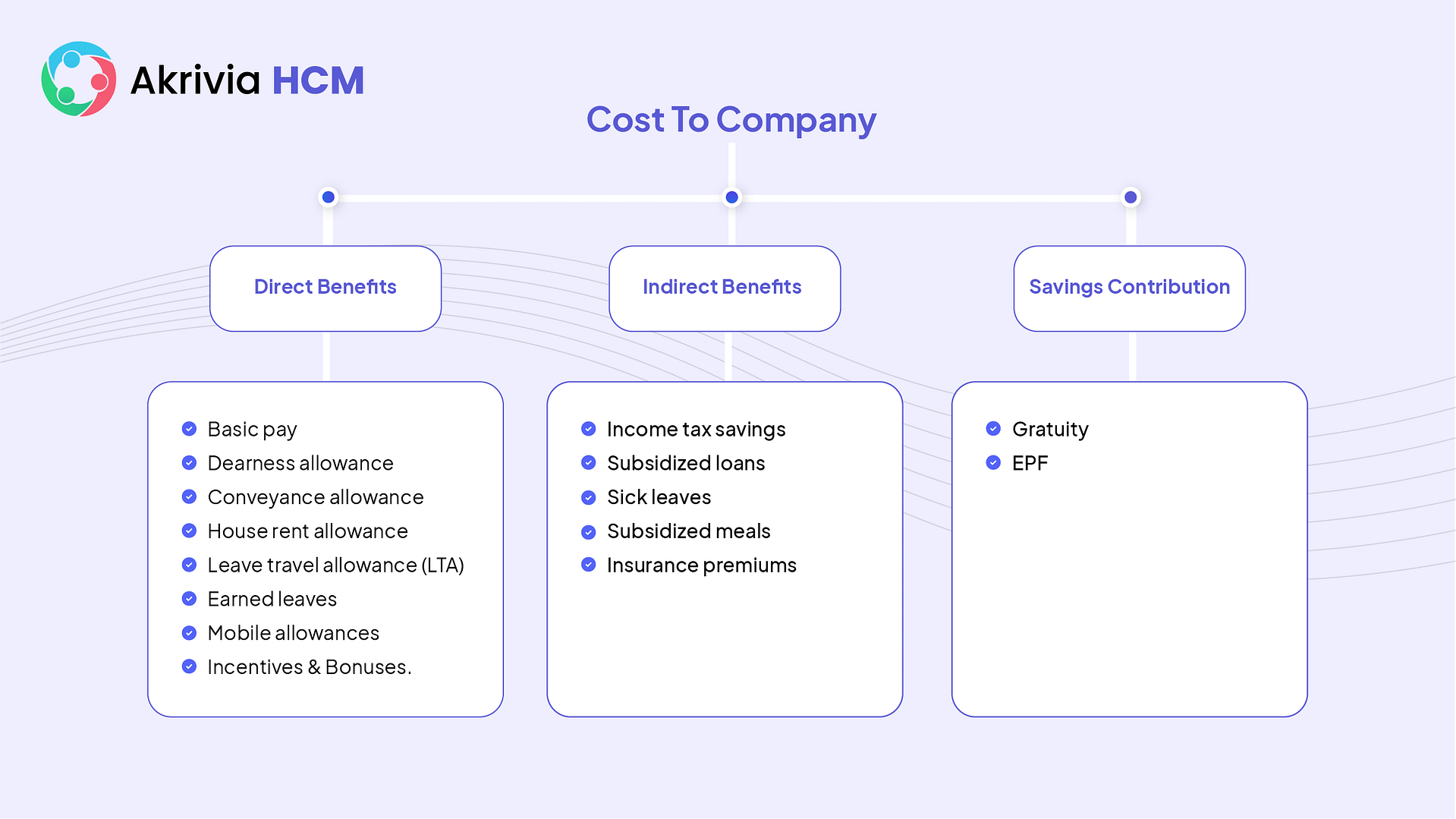
CTC is the sum of three vital components. These are direct benefits, indirect benefits, and saving contributions.
The direct benefits are the allowances paid in cash form. These are basic pay, dearness allowance, conveyance allowance, House rent allowance, leave travel allowance that is LTA, earned leaves, mobile allowances, incentives, and bonuses.
The indirect benefits include income tax savings, subsidized loans, sick leaves leased accommodation provided by the company, subsidized meals and food coupons, insurance premiums paid by the company, etc. Saving contributions include gratuity and EPF.
For example,
Mr. A applied in firm B for a vacant job position and was selected. He received a CTC of 900,000 rupees, and his annual CTC breaks up looks like this:
| Basic Salary | 500,000 |
| Medical Allowance | 55,000 |
| House Rent Allowance | 45,000 |
| Mobile and telephone allowance | 20,000 |
| Travel Allowance | 60,000 |
| Leave and Travel Allowance | 40,000 |
| Dearness allowance | 66,371 |
| Provident Fund Contribution | 84,000 |
| Gratuity | 29,629 |
It represents the total of direct benefits (such as employee yearly salary), indirect benefits (such as perks), and saving contributions (such as retirement or investment plans). The benefits include bonuses, statutory compliance, and allowances.
Basic salary in CTC refers to the fixed pay received by the employee before any additional payments and deductions. It is the minimum amount of money earned by the employee. It excludes overtime pay, bonuses, allowances, and other compensatory benefits.
The basic salary is taxable. Other components in the payslip like PF, ESIC, and Gratuity are calculated based on the basic pay. The basic salary is a part of the net salary or taking a home salary.
The employers maintain a timesheet to record time in and out of employees to calculate incentives and rewards. The additional earnings of an employee from overtime will not increase his basic salary.
Gross salary
Gross salary refers to an employee’s yearly/monthly salary before deductions. The components of the gross wage include basic pay, allowances, and perquisites.
Gross salary = Basic pay + allowances + perquisites
The components that do not include calculating gross salary in a payslip are gratuity, free snacks, meals, travel allowance, medical insurance, and leave encashment applicable during retirement.
An employee’s taxable salary in India is derived after making deductions in the gross pay. As per the rule of 80C, the person is liable to pay taxes on a gross salary after deductions like PF, LIC, PPF, and Mutual fund.
Considering the above table showing the CTC of Mr. A, his gross salary would be
Gross salary of Mr. A = 900,000 – (84,000 + 29,629) = INR 786,371
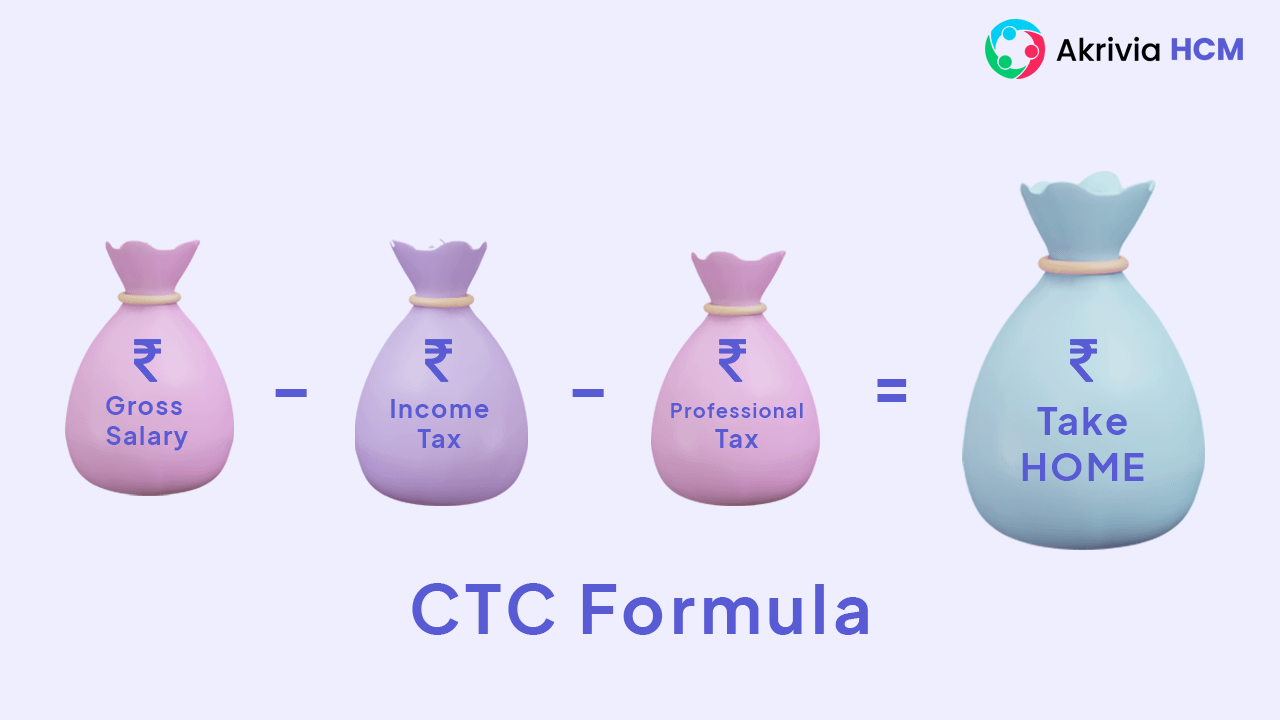
Net salary or take-home salary
Net salary refers to the employee’s net pay after deducting the gross salary amount. Some deductions are mandatory, and some depend on the employer policy.
Net salary = Gross salary – Income-tax (TDS) – Professional tax – Gratuity – EPF
Income tax is generally TDS (tax deducted at the source), and professional tax on earning individuals gets deducted from gross salary. EPF(Employee provident fund) is a type of pension scheme in India and gratuity is a monetary benefit rewarded as a token of appreciation to employees.
To calculate your taxable income, you must subtract certain deductions from your gross salary. Steps to follow:
Step 1: To calculate your gross salary, add HRA (house rent allowance), DA (Dearness Allowance), travel allowance, and special allowance to your basic salary.
Step 2: You’ll need to take professional tax, HRA exemptions, and standard deductions from your gross salary.
Step 3: Include any commissions/bonuses, interest-related income, etc., in the total amount.
Step 4: Then, deduct various expenses listed in Section 80C, 80D, and Chapter VIA of the Income Tax Act.
Step 5: Your taxable income is the amount that determines your income tax bracket and rate.
ECTC(Expected Cost to Company) stands for the total salary package a job seeker expects when they are willing to join a company. Once the individual gets hired, ECTC becomes CTC.
Gross salary is an employee’s total salary before deductions, such as taxes, insurance, or retirement contributions. It includes the base salary as well as any bonuses, allowances, and other benefits.
On the other hand, the cost to company (CTC) is the total amount of money an employer spends on an employee in a year. It includes the employee’s gross salary and other expenses such as employer contributions to insurance plans, provident funds, bonuses, and other benefits like transportation, housing, or meals.
Cost to Company is the total amount a company spends on an employee in a year, including the salary and other benefits.
On the other hand, the Take-home salary is the net amount an employee receives after all the deductions like taxes, Employee Provident Fund (EPF), Professional Tax, and any other statutory deductions.
Akrivia HCM Payroll Software can reduce the hassle of managing payroll for businesses with high employee turnover. This system can also reduce the time and cost associated with calculating employee salaries at the required CTC, thereby staying compliant with government regulations. This solution saves users time by making complex work easy and fast. As businesses face increasing demands to perform complex, labor-intensive tasks, automation offers a way to save time and increase overall efficiency.
Let’s Recruit, Reward, and Retain
Your Workforce Together!
